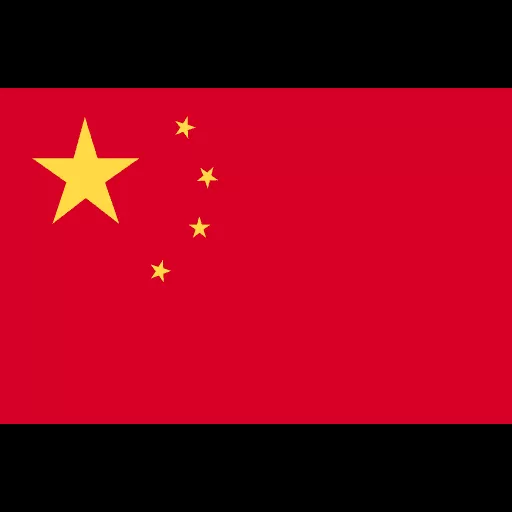
Tainless steel material cnc- one-stop parts processing
CNC machining stainless steel
Due to the special properties of stainless steel such as corrosion resistance and wear resistance, it has become one of the materials often chosen by engineers.
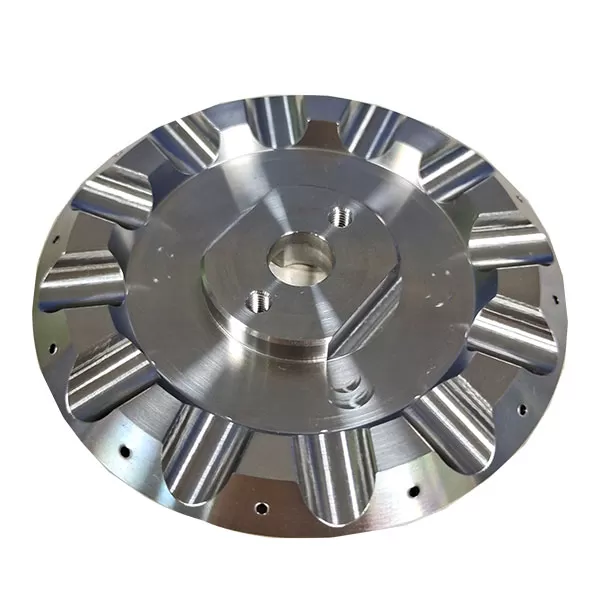

Common models of stainless steel are: Austenitic, martensite, 304, 303, 316, 420, duplex stainless steel, etc., different types of stainless steel physical properties are different, if your product needs non-magnetic and has high toughness and plasticity, but do not mind strength, it is recommended that you use austenitic stainless steel, if your product is food, it is recommended that you use stainless steel 316, HXC has more than ten years of CNC machining experience in stainless steel, when you are not ready to choose the material, please feel free to consult our online technical engineers.
What are the processing processes for CNC machining stainless steel parts?
Stainless steel density, high hardness, and no magnetic absorption, in the processing technology, clamping and tool selection will be different from other materials, general CNC machining stainless steel parts common processing technology are: CNC milling machine processing, CNC lathe processing, grinding machine processing, wire cutting, electric discharge, deep hole drilling. There are many new and precise processes, and engineers have ways to combine different processes to provide you with the ideal product.
Display of Stainless Steel Parts:
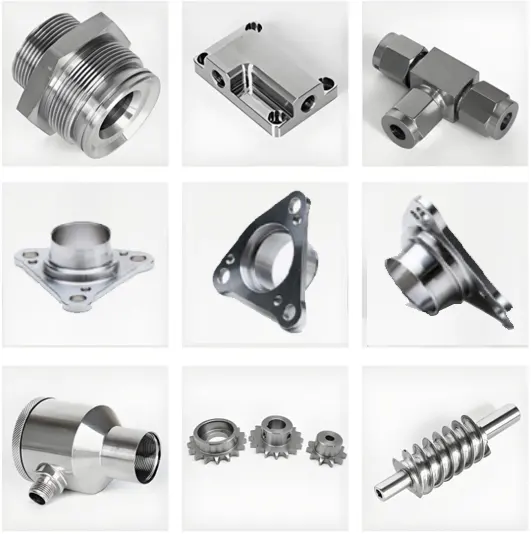

What are the surface treatments of CNC machining stainless steel?
Usually we will think that stainless steel will not be oxidized, corrosion, so there is no need to do any surface treatment, it is wrong, stainless steel in a certain environment, too long time will be oxidized, corrosion, but the speed is not faster than other steel parts.
In order to protect products, prevent oxidation, corrosion, improve product life and identification, we provide customers with processing + surface treatment services for a long time, usually CNC stainless steel after the common surface treatment are: grinding, polishing, sandblasting, powder spraying, wire drawing, electroplating, radium carving and so on.
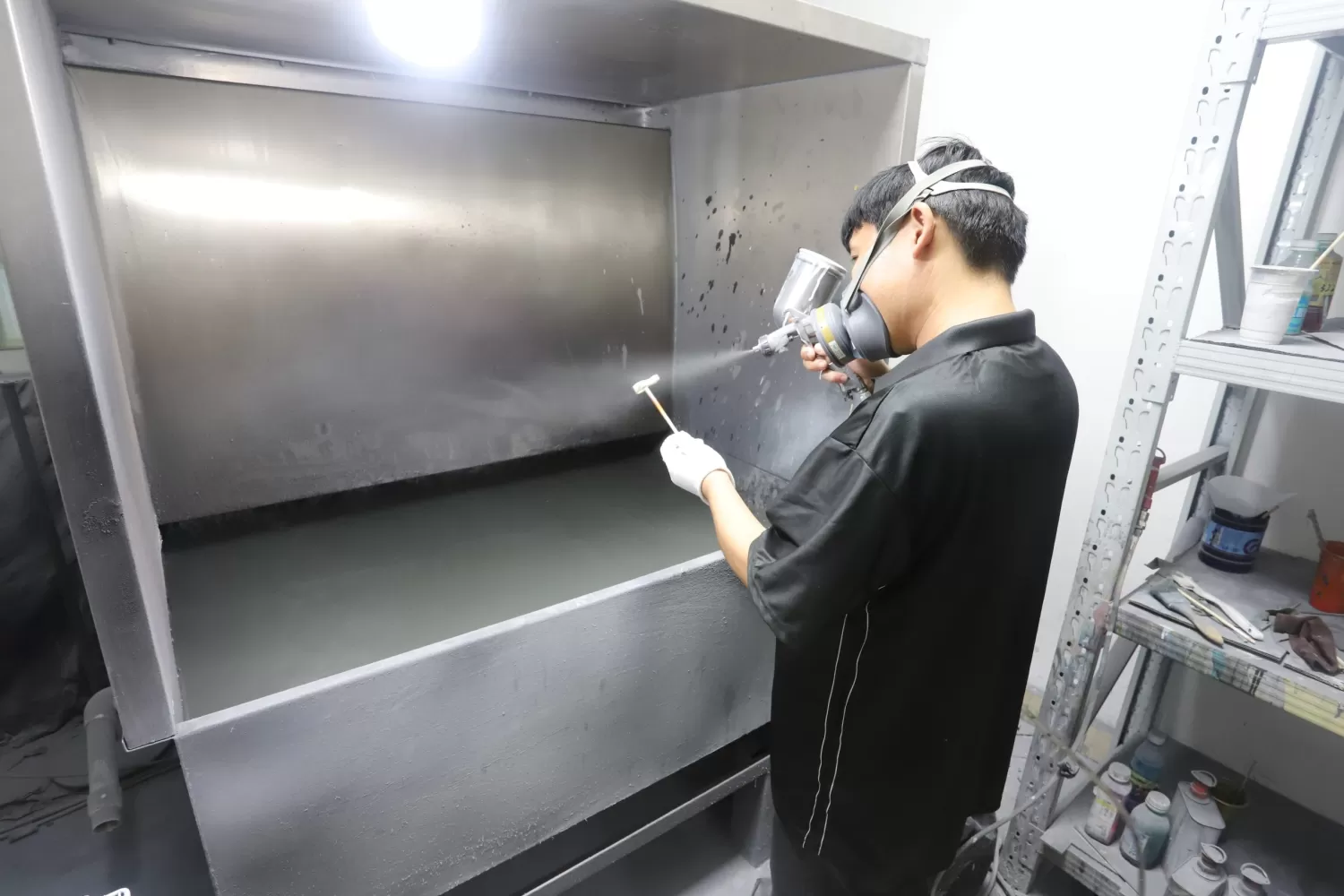

Detection Standards and Procedures
1:Formulate a detection plan according to the application of the parts and industry standards (such as ASTM, ISO, GB, etc.).
2:Sampling Inspection: For parts produced in batches, sample according to a certain proportion to ensure the overall quality stability.
3:Recording and Traceability: Preserve the detection data to achieve the quality traceability of the parts.
4:For products with strict requirements on product quality, we adopt the method of comprehensive inspection

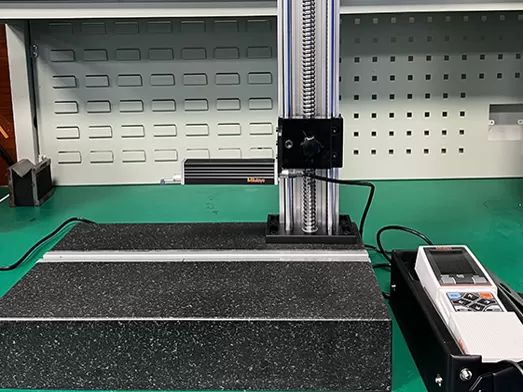

1.Detection of Dimensions and Geometric Precision
Tools: Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM), caliper, micrometer, projector, profilometer, etc.
Detection Contents:
Measure key dimensions of the parts, such as length, diameter, hole diameter, wall thickness, etc.
Check geometric tolerances, such as straightness, flatness, roundness, perpendicularity, coaxiality, etc.
Verify the geometric precision of complex curved surfaces or irregularly shaped structures through 3D scanning or image measurement.
2.Detection of Surface Quality
Appearance Inspection:
Visually observe or with the aid of a magnifying glass or microscope to check whether there are defects on the surface, such as scratches, cracks, oxidation, rust, burrs, pits, etc.
Check whether the effects of surface treatments (such as polishing, electroplating, sandblasting, etc.) are uniform.
Detection of Surface Roughness:
Use a surface roughness tester (such as a stylus type or optical type) to measure the surface roughness values (Ra, Rz, etc.) to ensure they meet the technical requirements.
3.Detection of Material Properties
Hardness Test:
Use a Rockwell hardness tester (HRB, HRC), Vickers hardness tester or Brinell hardness tester to check whether the hardness of the stainless steel meets the standards.
Chemical Composition Analysis:
Use a spectrometer (such as an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer, direct reading spectrometer) or chemical analysis method to verify whether the composition of the stainless steel (such as the contents of chromium, nickel, molybdenum) meets the requirements of the grade.
Mechanical Property Test:
Detect the mechanical properties of the stainless steel, such as strength and toughness, through tensile tests, impact tests, etc.
4.Detection of Internal Defects
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
Ultrasonic Testing: Used to detect internal defects such as cracks, pores, inclusions, etc., and is suitable for thick-walled parts.
X-ray Testing: Detect internal structural defects (such as weld quality, casting defects) by imaging through the penetration of the parts.
Magnetic Particle Testing: For ferromagnetic stainless steel, detect cracks on the surface and near the surface.
Penetrant Testing: Used to detect surface open defects (such as cracks, porosity) of non-porous materials.
5.Functional Testing
Sealability Test:
For parts with sealing requirements (such as valves, pipe joints), conduct hydraulic or pneumatic pressure tests to check for leakage.
Corrosion Resistance Test:
Verify the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel in specific environments through salt spray tests, intergranular corrosion tests, etc.
Assembly Test:
Check whether the assembly and fitting of the parts with other components are smooth to ensure normal functionality.