重力铸造浇注系统中的气泡跟踪
2025-03-08
压铸铝汽车零件的高效去毛刺和磨削方法
2025-03-19球墨铸铁件覆砂缩孔原因及改进工艺
摘要:
- 根据球墨铸铁的凝固特性及其在凝固过程中的体积变化,提出了生产球墨铸铁零件的铁模覆砂铸造工艺也需要收缩补偿的观点。在工艺设计中,应充分利用铁模铸件的良好刚性,更有效地发挥球墨铸铁石墨化膨胀的自收缩补偿特性。分别采用无冒口法、顺序凝固法、直接实用冒口法、平衡凝固法、冷冒口法、激冷法和数值模拟技术,并通过几个实例详细阐述了防止铸件收缩和缩孔的工艺措施。
球墨铸铁具有强度高、韧性好、成本低等优点,广泛应用于汽车、农业机械、船舶、管道、水力机械等重要制造业。然而,球墨铸铁零件的收缩和收缩缺陷一直是生产中的一个突出问题。铁模砂型铸造是在金属型铸造和壳型铸造的基础上发展起来的一种新型铸造技术。
由于由铁模和砂型组成的模具具有良好的刚性、快速冷却和良好的砂型密度,因此生产的铸件具有尺寸精度高、加工余量小、表面质量好、内部结构致密、产品质量一致性好的优点。特别是对于球墨铸铁零件,可以充分利用石墨化膨胀来发挥其自收缩特性。然而,这并不意味着用铁模砂涂层铸造的球墨铸铁零件不会有收缩缺陷,并且可以在没有冒口的情况下铸造。本文基于球墨铸铁的凝固特性,结合数值模拟技术,介绍了防止铁模覆膜铸造过程中缩孔和缩孔的各种方法和成功案例。
一
国内外铸造工人对球墨铸铁进行了数十年的研究,发现它与其他合金具有不同的凝固特性,主要表现在以下几个方面:
(1) 球墨铸铁的共晶凝固范围相对较宽。当球墨铸铁发生共晶结晶时,由于镁的加入,石墨芯在液相中生长到一定尺寸时,被奥氏体包围。由于奥氏体壳阻碍了碳原子从熔融液体扩散到石墨球,石墨球的生长速度减慢,凝固过程缓慢进行,从而在新的石墨异质核上形成了一个新的石墨核,其过冷程度更高,以保持共晶凝固。因此,共晶转变发生在相对较宽的温度范围内,导致铸件宽截面上的固相和液相共存,以糊状凝固,难以补偿凝固过程中的收缩。
(2) 球墨铸铁有许多石墨芯。与灰口铸铁相比,球墨铸铁必须经过球化和孕育处理。它的石墨芯比灰铸铁多得多,共晶团的尺寸比灰铸铁细得多。
(3) 球墨铸铁在凝固过程中具有较大的石墨化膨胀力。在共晶凝固过程中,球墨铸铁的石墨迅速被奥氏体壳包围。石墨生长引起的膨胀不能传递到铁水中,导致共晶膨胀力较大。石墨化膨胀力是灰口铸铁的5倍。如果模具的刚度不高,就会导致模具膨胀,铸件的形状也会膨胀。石墨化膨胀力被释放,减少了凝固和收缩过程中对金属的收缩补偿作用,从而增加了缩孔和收缩倾向。
(4) 球墨铸铁凝固过程的体积变化模式分为三个阶段:从铁水填充到共晶温度的液体收缩;共晶凝固过程中石墨球沉淀引起的体积膨胀;铁水凝固后冷却过程中的体积收缩。
国内外专家提出了许多球墨铸铁凝固过程中体积变化的计算方法。一汽西柴高级工程师周根在以往计算方法的基础上提出了一种新的计算方法:对于w(Si)含量为2.5%的铸铁,共晶奥氏体的w(C)含量为1.54%~1.6%;如果铁水含有3.8%的碳和2.5%的硅,石墨沉淀量为3.8%-(1.54~1.6)%=(2.2~2.26)%,膨胀率为4.4%~4.52%(每1%石墨沉淀的体积膨胀率为2.02%≈2%)。浇注温度为1350℃,共晶温度为1150℃,消除浇注系统中50℃的温降,过热为150℃,液体收缩率按液体收缩率(1.6~1.8)%/100℃计算,液体收缩为2.4%~2.7%,金属凝固收缩率按非石墨化钢的3%数据计算,则总收缩率为5.4%~5.7%。如果浇注温度更高,总收缩率会更大,这显然不能被石墨化膨胀完全抵消。因此,无论采用何种工艺,球墨铸铁零件总是需要补偿收缩。只要模具刚度足够,认为球墨铸铁不会收缩的观点是错误的,铁模砂型铸造工艺也不例外。
二
铸造CAE技术利用计算机及相关软件对铸件的充型和凝固过程进行数值模拟,并对获得的数据进行处理和分析,以预测缺陷和优化工艺。
充型模拟模拟了铸造模具中熔融金属流动过程对铸件成形的影响。熔融金属的平稳流动和合理的填充顺序是保证铸件质量的重要条件,也是合理凝固顺序的先决条件。通过填充模拟,可以分析熔融金属在浇注和提升管系统中的流动状态,优化浇注和提升板系统,避免熔融金属的流动分离,减少熔融金属对模型的冲刷和侵蚀。凝固过程是熔融金属填充型腔后从液体转变为固体的过程。通过凝固模拟,可以分析铸件中熔融金属的凝固顺序,并预测凝固过程中出现的缺陷。
目前,数值模拟技术已广泛应用于铸造工艺设计。与一般砂型铸造工艺相比,铁模覆膜铸造工艺的传热过程相对复杂,包括“铸砂覆膜铁模气氛”之间的传热。经过实验和生产实践的验证,该工艺的仿真分析也相对成熟可靠。
三
铁模覆膜铸造工艺的两个主要特点是:① 模具刚性好; ② 调整模具各部分的砂涂层厚度,可以在一定程度上提高各部分的冷却速度。因此,在工艺设计中应充分利用其优势。对于球墨铸铁零件,良好的模具刚度可以更有效地发挥其石墨化膨胀的自补偿特性。一般认为,在不发生石墨浮起和不发生一次石墨沉淀的前提下,w(C)和w(Si)的量越高,孕育效果越强,越有利于石墨化,石墨化膨胀越大,自补偿效果越好。
然而,如上所述,无论模具刚度有多好,球墨铸铁零件总是需要补偿的。在铁模砂涂覆过程中,有几种方法可以防止铸件缩孔和收缩,并通过实例进行了说明。
3.1无立管法
The riserless method is to use the pouring system to carry out liquid shrinkage compensation, and maximize the use of graphitization expansion to complete self-shrinkage compensation. The iron mold sand coating process was first successfully applied to the production of crankshafts, and the riserless casting of crankshafts is also the most typical. Its process feature is the use of a thick pouring system to provide liquid shrinkage compensation for the casting. The riserless method is suitable for ductile iron castings with a casting modulus of >2.5 cm. It requires high metallurgical quality of molten iron, a small flat and thin ingating channel, and the introduction of molten iron at multiple points. In the absence of cold shut of the casting, the pouring temperature should be low.
Figure 1 shows the liquid phase area of the Steyr 615 crankshaft when it solidifies 30% after pouring. It can be seen from the figure that in the early stage of solidification, the ingating channel on the crankshaft fan plate has been closed, and the center of the main journal and the connecting rod journal has formed an overall thick liquid phase area. In the later stage, self-shrinkage compensation is completely achieved by graphitization expansion.
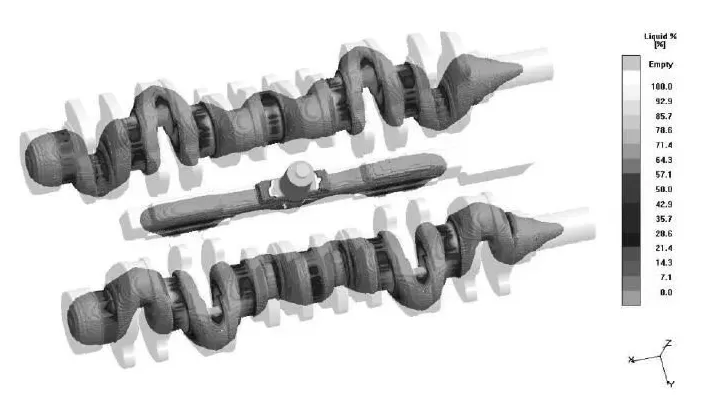
图1铸件凝固30%时的液相显示
3.2顺序凝固法
The riserless method is to use the pouring system to carry out liquid shrinkage compensation, and maximize the use of graphitization expansion to complete self-shrinkage compensation. The iron mold sand coating process was first successfully applied to the production of crankshafts, and the riserless casting of crankshafts is also the most typical. Its process feature is the use of a thick pouring system to provide liquid shrinkage compensation for the casting. The riserless method is suitable for ductile iron castings with a casting modulus of >2.5 cm. It requires high metallurgical quality of molten iron, a small flat and thin ingating channel, and the introduction of molten iron at multiple points. In the absence of cold shut of the casting, the pouring temperature should be low.
Figure 1 shows the liquid phase area of the Steyr 615 crankshaft when it solidifies 30% after pouring. It can be seen from the figure that in the early stage of solidification, the ingating channel on the crankshaft fan plate has been closed, and the center of the main journal and the connecting rod journal has formed an overall thick liquid phase area. In the later stage, self-shrinkage compensation is completely achieved by graphitization expansion.
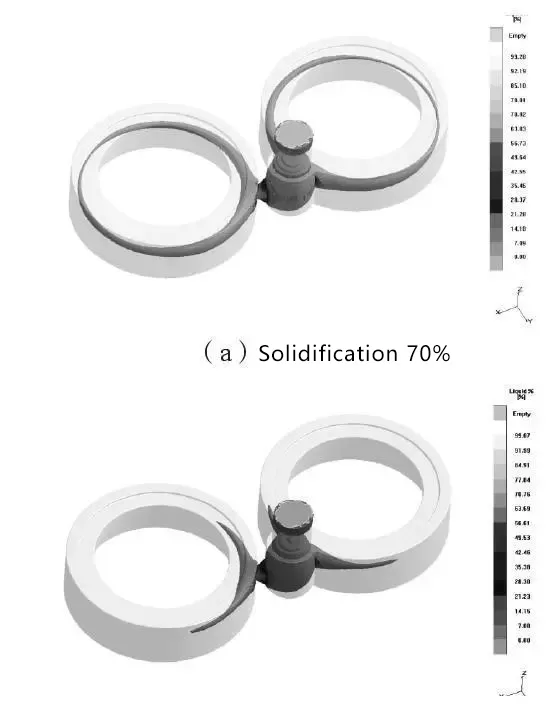
图2牵引轮凝固过程
3.3直接实用立管法
The direct practical riser method uses a riser to compensate for the liquid shrinkage of the casting. When the liquid shrinkage stops or the volume expansion begins, the riser neck or the inner gate solidifies in time, so that the eutectic expansion in the casting mold puts the molten metal under positive pressure to prevent vacuum inside the casting. The direct practical riser is suitable for ductile iron castings with a casting modulus <2.5 cm. The casting process has a high yield rate and the riser is easy to remove.
The bearing cover weighs 3.6 kg per piece, with an outline size of 118 mm×110 mm×60 mm. The material is QT500-7. When the iron mold sand casting process is used, 14 pieces are arranged in one mold. The casting is liquid-compensated using a direct practical riser. Figure 3 shows the liquid phase area when the bearing cover is 60% solidified after pouring. As can be seen from the figure, the riser neck has solidified at this time, and the liquid metal in the casting and the riser has been disconnected. The yield rate of this process reaches 76.5%, which is 25% higher than the yield rate of clay sand casting (51.5%).
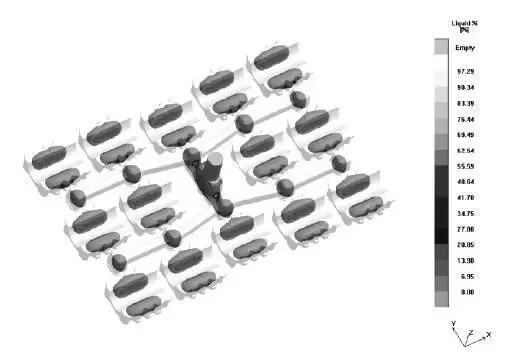
图3:铸件凝固60%时的液相显示
3.4平衡凝固法
平衡凝固理论认为,冒口在铸铁中的作用只是为了补偿铸件冷却和凝固引起的膨胀和收缩差异。冒口不必晚于铸件凝固。核心是:冒口应远离热点,靠近热点,以减少冒口对铸件的热干扰,促进收缩补偿。
转子材料为QT500-7,铸件长628mm,宽195mm,中间筒体直径65mm。中间筒体与两个侧板相交形成热点。采用平衡凝固法将冒口设置在截锥靠近热点的一侧,平内流道面向圆柱体内径,避免铁水直接填充热点。图4显示了转子铸件在浇注后凝固85%。从图中可以看出,中间圆柱体的热点处即将形成一个孤立的液相区域。该液相区域的体积收缩被后期凝固过程中的石墨化膨胀所抵消。
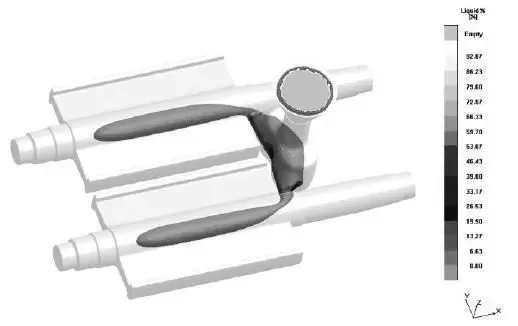
图4显示了铸件凝固85%时的液相
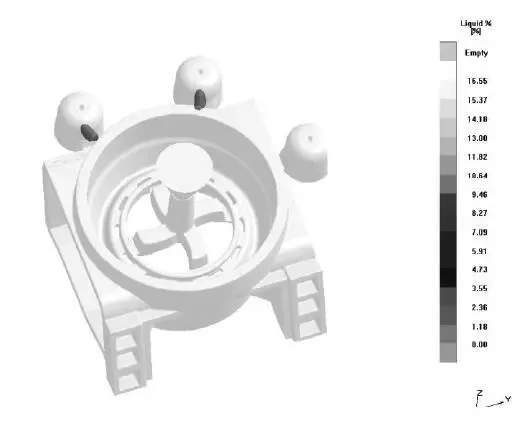
图5铸件凝固97%时的液相显示
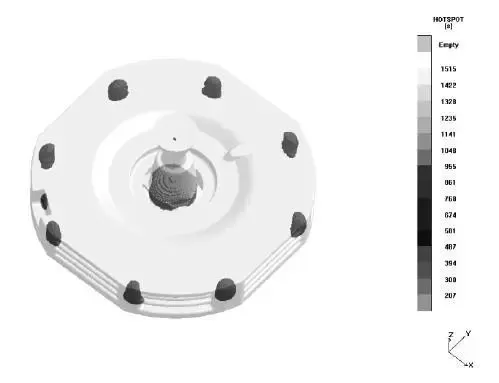
图6热段显示
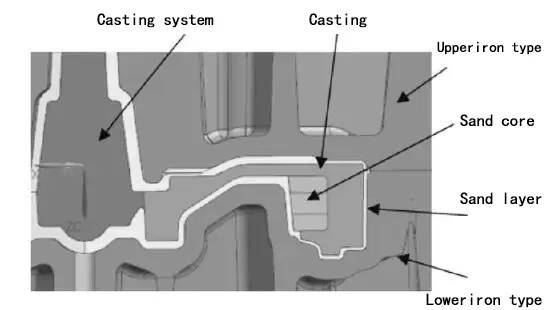
图7电机端盖工艺设计
四
(1) 铁模覆砂铸件具有良好的模具刚性、快速冷却和良好的覆砂密度。在生产球墨铸铁零件时,可以充分利用石墨化膨胀来发挥其自补偿特性。然而,根据球墨铸铁的凝固特性和凝固过程中体积的变化,可以得出结论,铁模覆砂铸造工艺也需要补偿球墨铸铁零件的收缩。
(2) 与一般砂型铸造工艺相比,铁模覆砂铸造工艺的传热过程相对复杂,包括“铸砂覆铁模气氛”之间的传热。经过实验和生产实践的验证,该工艺的仿真分析相对成熟可靠。
(3) 铁模具有良好的模具刚性,能有效发挥其石墨化膨胀的自补偿特性。在不发生石墨浮起和不发生一次石墨沉淀的前提下,C和Si含量越高,孕育效果越强,效果越好。
(4) 使用无冒口法、顺序凝固法、直接实用冒口法、平衡凝固法、冷冒口法和激冷法等各种方法防止铸件收缩缺陷的成功案例表明,有必要对各种铸件的铁模覆膜铸造工艺进行具体分析和设计。