Silikonform: Zeit- und Arbeitsersparnis bei Serienfertigung in Kleinserie
2025-04-11
Automobil-Prototypenverarbeitung – Fallbeispiel: Scheinwerferrahmen
2025-04-14Automobil-Prototypenverarbeitung - Fallbeispiel: Gehäuseteile
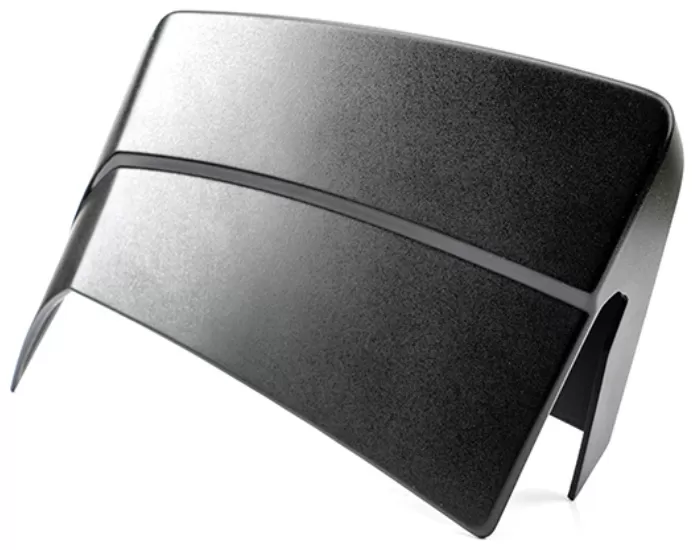

Verfahren: Vakuumumformung
Material: PX5690 (ABS-ähnlich)
Maximale Präzision: 0,05 mm
Produktionszyklus: 1–2 Tage
Produktabmessungen: 48 cm × 19,5 cm × 9 cm
Nachbearbeitung: Mattierung durch Sprühlackierung
Fallbeschreibung
Das Prototyping von Automobil-Gehäuseteilen ist ein wichtiger Schritt im Automobilherstellungs- und Designprozess. Es beinhaltet die Erstellung physikalischer Modelle oder Prototypen, die zur Überprüfung des Aussehens, der Maße, der Passform und der Funktionalität neuer Designs verwendet werden. Das Prototyping wird normalerweise vor der Serienfertigung durchgeführt, um sicherzustellen, dass das Design allen technischen und qualitativen Anforderungen entspricht. Im Folgenden wird der allgemeine Prozess des Prototyps für Automobil-Gehäuseteile beschrieben:
Entwurf und Modellierung: Mit CAD-Software (Computer-Aided Design) werden detaillierte Konstruktionspläne für Fahrzeugkomponenten erstellt. Diese Zeichnungen enthalten alle erforderlichen Maße, Formen und Anschlussdetails.

Materialauswahl: Entsprechend dem Verwendungszweck und den Eigenschaften des Prototyps wird das geeignete Material gewählt, beispielsweise ABS-Kunststoff, Polyurethan, Verbundwerkstoff oder Metall.
Fertigungsverfahren: Abhängig von der Konstruktionskomplexität und Stückzahl wird eine geeignete Rapid-Prototyping-Technologie gewählt, beispielsweise Stereolithographie (SLA), selektives Laserschmelzen (SLM), CNC-Fräsen oder Drehen.

Nachbearbeitung: Nach dem Rapid-Prototyping können Schleifen, Spachteln, Lackieren, Polieren oder andere Oberflächenbehandlungen erforderlich sein, um das Erscheinungsbild und die Haptik des Prototyps zu verbessern.
Montage und Prüfung: Der Prototyp wird am Fahrzeug zur praktischen Montageprüfung installiert, um seine Passgenauigkeit, strukturelle Festigkeit und funktionale Leistung zu überprüfen.

Bewertung und Optimierung: Basierend auf den Testergebnissen werden notwendige Modifikationen und Optimierungen am Prototyp vorgenommen, bis die Design- und Technikstandards erfüllt sind.
Finale Freigabe: Nach Bestehen aller Tests und Erfüllung aller Anforderungen kann der Prozess zur nächsten Stufe übergehen, beispielsweise zur Herstellung von Serienproduktionswerkzeugen und Produktionsvorbereitung.
Das Prototyping von Automobil-Gehäuseteilen hilft nicht nur, potenzielle Designprobleme zu identifizieren, sondern liefert auch physikalische Muster, mit denen Ingenieure und Designer eine direkte Evaluierung und Verbesserung durchführen können. Dieser Prozess ist unverzichtbar, um die Endqualität des Produkts zu gewährleisten, Entwicklungszyklen zu verkürzen und Kosteneinflüsse zu steuern.